Introduction
Vacuum era is one of the maximum huge medical and industrial upgrades of the modern technology. From area research to semiconductor manufacturing, from meals safety to superior scientific system, the feature of vacuum era is huge and transformative. Simply placed, vacuum generation is the technological know-how and engineering of creating, preserving, and measuring low-stress environments (under atmospheric strain).
In this specific manual, we are capable of cover:
- What is vacuum era?
- Historical history and evolution
- Basic standards and classifications
- Types of vacuum pumps and tool
- Applications in industries and every day life
- Advantages and barriers
- Future trends and innovations
- Important records summarized in tables
What is Vacuum Technology?
Vacuum technology is the have a look at and application of creating a vacuum—an environment in which the stress is extensively decrease than atmospheric pressure. It consists of several device which incorporates pumps, chambers, gauges, and sealing structures to reap and hold preferred vacuum tiers.
In medical terms, a vacuum does now not recommend a complete absence of count, however a circumstance wherein the quantity of debris steady with unit amount is lots less than at fashionable atmospheric strain (1 atm or 101,325 Pa).
Historical Evolution of Vacuum Technology
The development of vacuum generation has a protracted and fascinating records.
| Period | Key Development | Scientist/Inventor |
|---|---|---|
| 17th Century | First mercury barometer | Evangelista Torricelli (1643) |
| 17th Century | Vacuum experiments with air pumps | Otto von Guericke (1650s) |
| 19th Century | Development of mechanical pumps | Heinrich Geissler |
| Early 20th Century | Oil-sealed rotary pumps | Wolfgang Gaede |
| Mid 20th Century | Diffusion and turbomolecular pumps | Various inventors |
| Late 20th Century | Semiconductor & space applications | Global adoption |
| 21st Century | Nanotech, cryogenics, quantum computing | Modern advancements |
Principles of Vacuum Technology
The working principle of vacuum technology revolves round lowering air strain in a chamber the use of mechanical, chemical, or bodily method.
Key Parameters:
- Pressure Levels:
- Low vacuum (above 25 torr)
- Medium vacuum (1–25 torr)
- High vacuum (10⁻³ to 10⁻⁷ torr)
- Ultra-excessive vacuum (10⁻⁷ to ten⁻¹² torr)
- Extreme high vacuum (beneath 10⁻¹² torr)
- Vacuum Creation:
- Removing molecules the use of pumps
- Preventing leaks with seals
- Measuring vacuum levels the usage of gauges
- Important Concepts:
- Mean Free Path: Average distance a molecule travels earlier than colliding.
- Outgassing: Release of trapped gases from materials indoors a vacuum chamber.
- Leak Detection: Ensuring no outside fuel enters the chamber.
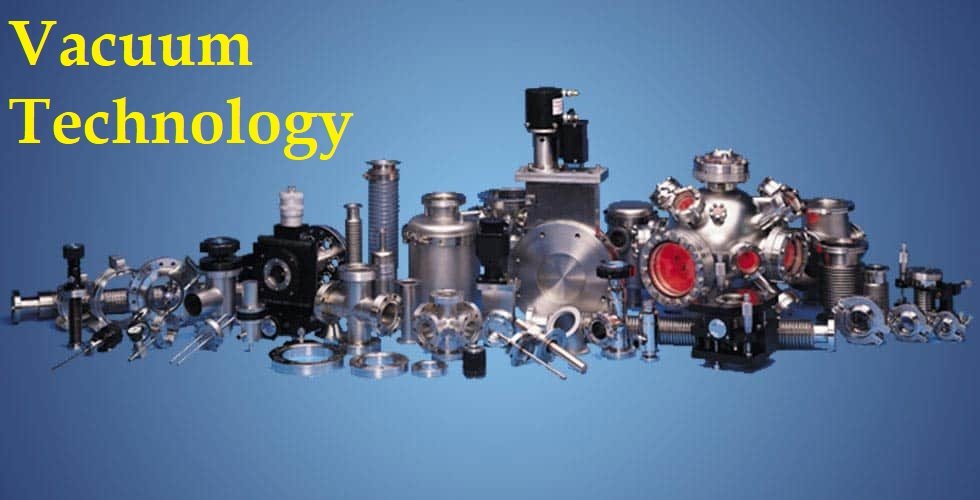
Types of Vacuum Pumps
Vacuum pumps are the backbone of vacuum era. They get rid of air/gasoline molecules to create a strain beneath atmospheric degree.
| Type | Working Principle | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Rotary Vane Pump | Uses rotating vanes in oil-sealed chamber | Laboratories, medical equipment |
| Diaphragm Pump | Flexible diaphragm moves to displace air | Clean applications, analytical labs |
| Roots Pump | Uses lobes to trap and move air | Chemical processing, metallurgy |
| Diffusion Pump | Uses vapor jet to direct molecules | High vacuum for coating & research |
| Turbomolecular Pump | High-speed turbine blades | Semiconductor industry, physics research |
| Cryogenic Pump | Cools gases to low temperatures | Space simulations, particle accelerators |
Applications of Vacuum Technology
Vacuum generation has widespread packages throughout industries, technological know-how, and each day lifestyles.
1. Industrial Applications
- Semiconductor Industry: Chip manufacturing requires extremely-smooth high vacuum environments.
- Metallurgy: Vacuum furnaces for refining metals and producing alloys.
- Coating Technology: Thin-movie coatings on glass, mirrors, sun panels, and decorative items.
- Energy Industry: Used in nuclear fusion experiments and hydrogen garage.
2. Scientific Applications
- Space Research: Simulating outer region environments for satellites and rockets.
- Particle Physics: Large accelerators like CERN rely upon extraordinarily-immoderate vacuum chambers.
- Medical Research: Vacuum used in MRI machines, freeze-drying, and sterilization.
3. Daily Life Applications
- Food Industry: Vacuum packaging to extend shelf life.
- Household Appliances: Vacuum cleaners (although they use suction in place of excessive vacuum).
- Electronics: CRT presentations, mild bulbs, and plasma TVs.
Advantages of Vacuum Technology
- Enables smooth and contamination-unfastened environments
- Essential for present day semiconductor and nanotechnology studies
- Increases product shelf lifestyles (meals packaging)
- Reduces oxidation in the course of metallurgical procedures
- Supports area exploration and advanced physics
Limitations and Challenges
- High equipment and protection fees
- Requires professional operation and leak detection
- Outgassing can contaminate structures
- Power-sizable for extremely-high vacuum systems
- Limited scalability for a few industries
Future of Vacuum Technology
With fast advancements in nanotechnology, quantum computing, and renewable power, vacuum generation is predicted to play a more crucial position. Future innovations may moreover encompass:
- Integration with AI: Smart leak detection and device tracking.
- Green Technology: Energy-inexperienced vacuum pumps.
- Quantum Systems: Enabling strong environments for quantum computers.
- Space Colonization: Vacuum generation for existence-useful resource and manufacturing at the Moon/Mars.
Important Information in Table Form
Classification of Vacuum Levels
| Vacuum Level | Pressure Range | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Low Vacuum | 25 – 760 torr | Industrial drying, packaging |
| Medium Vacuum | 1 – 25 torr | Metallurgy, chemical processing |
| High Vacuum | 10⁻³ – 10⁻⁷ torr | Semiconductor manufacturing |
| Ultra-High Vacuum | 10⁻⁷ – 10⁻¹² torr | Particle accelerators, nanotech |
| Extreme High Vacuum | <10⁻¹² torr | Advanced space research |
Conclusion
Vacuum generation is a effective enabler of cutting-edge technological know-how and organization. From the arrival of microchips to exploring outer area, its significance can’t be overstated. As era evolves, vacuum systems becomes even extra sophisticated, power-green, and important for futuristic industries inclusive of quantum computing, AI-driven nanotechnology, and sustainable energy answers.
Understanding vacuum era isn’t always pretty much getting to know pumps and pressure—it’s approximately appreciating a hidden pressure that makes lots of modern-day innovation feasible.